Dosing plunger pump. Dosing pumps. Dosing pumps: description and reviews
All pumping equipment to one degree or another provides the ability to regulate the flow.
Regulation is carried out by feedback between the pump flow rate and the control mechanism. According to information from the device, the operator or automation acts on the actuating mechanism for regulating the flow (valve, variator, electric drive).
By the signal from the sensor. The frequency of injection of reagents from the pump depends on the current power, and the current strength is directly proportional to the difference between the required and actual signals from the sensor. Dosing pumps that operate in proportion to the received external signal are often called proportional.
Use of metering pumps. Dosing of coagulants and flocculants. Food industry. Chemical and petrochemical industry. Galvanic production and many, many others. The principle of operation of an adjustable electromechanical metering pump is based on a periodic change in the volume of the working chamber, forcing it to fill with liquid and displace the liquid from this chamber. The rotational movement of the electric motor by the worm gear, the eccentric roller and the spring is converted into the reciprocating motion of the rod connected to the piston or diaphragm.
The exception is dosage (dosing) with a built-in feed control scale, according to which the feed is adjusted with a given accuracy.
Typical design - pump ND, Ndr, designed for volumetric pressure regulation of neutral and aggressive fluids.
Pump ND, NDR - single-plunger, horizontal single-acting.
Electric motors, eccentric shaft are interconnected.
The gear worm wheel is rigidly fixed to the eccentric shaft. On the shaft neck of the metering (metering) pumps, the eccentric sets in motion a slider with a plunger of the hydraulic cylinder. By rotating the eccentric, you can steplessly change the eccentricity, the stroke length of the plunger and the feed from zero to maximum.
The hydraulic cylinder consists of a housing, a plunger, a suction, discharge ball valves, a sealing device with an annular flashlight designed to supply flushing fluid or a hydraulic shutter device.
The limit of lowering their reverse stroke allows you to adjust the feed rate to 0, 5% or 0, 2% in the range from 0 to 100%. The principle of operation of the electromagnetic metering pump is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction: inside the electromagnetic solenoid there is a spring rod that is connected to the piston or diaphragm of the working chamber. When the current passes through the electric circuit, the rod moves inward into the solenoid, when the circuit breaks, the spring pushes it. The mutual movement of the rod leads to a change in the volume of the working chamber, its filling with liquid and the displacement of the liquid from it.
The regulating mechanism in the ND pump provides infinitely variable supply manually when the unit is stopped, in the NDR pump - manually on the stopped and running unit (on-the-go regulation).
The error in the regulation of domestic dosing (dosing) pumps lies in the range from 0.5 to 2.5% and higher.
Symbol
ND2.5 10/400 K14 A (B) U2, where:
ND - metering pump (dosing),
2.5 - category accuracy regulation,
10 - feed l / hour,
400 - pressure kgf / cm²,
K - flow part of chromium-nickel steel,
1 - without a cooling or heating jacket,
4 - with a supply of flushing, coolant,
A - general industrial (sometimes “A” is lowered) electric motor, (B) - explosion-proof,
U - climatic modification of dosing (dosing) pumps,
2 (3, 4) - category of accommodation.
In manual mode, the frequency of turning the circuit on and off is regulated, in the flow mode, the signal is supplied by the flowmeter sensor. From the Greek peristalsis - covering and press. The principle of operation of the peristaltic dosing pump is based on the roller press of the tube in which the dosed liquid is located and the shift of the clamping point. Adjusting the amount of fluid supplied by changing the speed of rotation of the wheel using the rollers.
WATER DEVICES WITH PULSE OUTPUT. The main components of the pulsed output water meters are a removable magnet and a sensor installed in the normal open position: any movement of the magnet connects the socket. The number of pulses is proportional to the flow in the pipeline. To ensure the accuracy of measurements, it is necessary to install the flow meter in a straight line of the pipeline. The length of the straight pipe section in front of the flowmeter must be at least eight nominal diameters. The length of the straight section of the pipe after the flowmeter must be at least three nominal diameters.
Specifications
Sealing unit - cuffed from rubber or ftoroplast.
Permissible vacuum gauge suction height not more than 2-3 m.
Dosing pumps (dosing) have self-priming. Self-priming height about 1 meter.
The mechanism for changing the stroke length of the plunger in dosing (dosing) pumps ND, NDr differs from GND, NDG.
The cam, during rotation, pushes the slider and piston towards the valve body. In the opposite direction, the piston is pushed out by a spring. The outer sleeve of the slide, moving relative to the axis of the cam, with the help of an adjustable screw limits the stroke of the suction of the plunger, i.e. changes the stroke length of the slider and adjusts the feed.
Otherwise, inaccuracies in measurements caused by turbulence of the flow in the pipeline are possible. Before the flowmeter, it is advisable to install a coarse filter. Typical technical characteristics of water flow meters are presented in the tables. Watertight screwdrivers with threaded connection.
Turbine flow meters with flange connection. Dosing principles, types of dosing pumps, modern control options. Dosing pumps belong to the family of positive displacement pumps. Most often they have a diaphragm type, which means that the specifics of their work is the absence of leakage. The reason is that the diaphragm serves as a seal between the transmitted fluid and the environment. Diaphragm pumps have two valves - one on the suction and pressure sides. The principle of operation of diaphragm pumps consists in the absorption of a certain volume of liquid through a suction valve, which in the reverse stroke of the membrane is pushed through the exhaust valve to the pressure line.
Tightness is achieved by installing between the drive and the hydraulic part of the diaphragm head. The valve body consists of three chambers. The first is oil. In an intermediate liquid, neutral to product and oil. The third is working (product): medium circulates in it and working valves are located.
The feed chamber of the oil-filled chamber to protect the metering pump LP from increasing the discharge pressure is built into the plunger.
Constructive diaphragm pumps The diaphragm is driven by a piston in small diaphragm pumps. In turn, the piston is controlled by an electromagnet. Typical of large diaphragm metering pumps is that the diaphragm is driven by a piston, which is driven by an eccentric mechanism. It is powered by a standard induction motor. There is another type of metering diaphragm pump. The diaphragm is driven by a piston, which is driven by a stepped or synchronous motor using a traction mechanism.
The control of the characteristics of the fluid pumping process in modern pumps is provided in manual and automatic modes. Depending on the requirements for operation, it may be necessary to take into account certain parameters. For example, the user can adjust the feed volumes and the intensity of the function. However, there are certain types of equipment that are specifically designed for the point service of certain environments. These include dosing pumps used in the food, pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
When using a stepper motor, the pump dynamics is significantly improved. In addition, its accuracy is increasing. With the described structure, there is no need to adjust the piston stroke, since it is directly connected to the diaphragm. The result is very good working conditions during suction and injection. Compared to conventional electromagnetic diaphragm pumps, which generate greater ripple both in flow and pressure, diaphragm pumps with a stepper motor are characterized by much more stable metering.
Features of dosing pump
Dosing units provide the possibility of volumetric pressure pumping of liquids, suspensions and emulsions. However, most of these pumps can serve both neutral and aggressive environments. For this reason, their use is common in the chemical industry. Depending on the characteristics of the material used in the flow part, the specific purpose of the equipment is determined. The main difference from traditional household units is that dosing pumps allow you to adjust the pressure level from the exit point to the entrance of the working medium. In this case, the absolute indicator of the inlet pressure exceeds the same indicator of the pumped liquid. Among the main technical and operational characteristics of such equipment, the ability to work with certain environments and the diameter of the passage of the nozzles is noted.
Technical characteristics of diaphragm pumps. The main characteristics of metering pumps are no different from pumps. The head of dosing pumps is characterized by the following feature: the pressure created by the pump is not created once, but gradually and has a precisely defined size. It is enough to overcome the counterparty. The flow rate is determined in two main ways - experimental or empirical.
Studies have shown that in most cases proportional dosing is used. Proportional dosing. To achieve the so-called proportional dosing, it is necessary that the dosing pump be connected to the flow meter. The figure shows a typical proportional metering system. The calculation of the cost of each dose is technically elementary.
Hose metering pumps
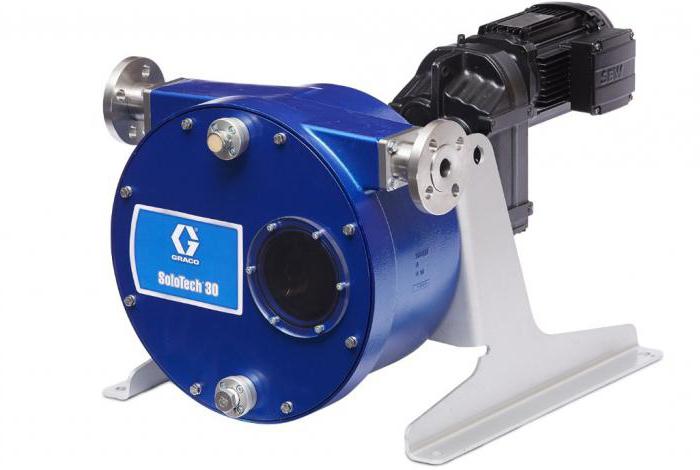

This type of metering pump is designed to work with liquids and pasty substances. The principle of operation is based on mechanical action on the working channel, which is most often represented by a strong but flexible tube. That is, during operation, mechanical pressure is applied to the hose with the medium, as a result of which the liquid is pushed to the outlet. As a physical activator, rollers rolling around the circumference are used. By design, metering pumps of this type are a device including flexible pipes and a hose with a set of rollers. Also, the infrastructure part is provided by the track into which the tube line is laid. It is in him that the physical effect occurs.
It is good to remember that solenoid pumps are very difficult to adjust the piston stroke according to the dose. The reason is that after each stroke change, the pump must be calibrated again. Positive dosing Proportional dosing is not a universal method. Typical examples are pH control systems and disinfection systems that do not use proportional dosing. Typical of these is that the dosage effect is measured using an appropriate pH sensor after acid dosing.
Depending on the measured value, an appropriate signal is supplied to the pump. This method is known as closed loop dosing. In these cases, the flow of water is approximately constant. Accordingly, the flow rate of the metering pump is proportional to the difference between the expected and actual chemical concentration. In applications where the water flow is not constant, both control methods are used in proportion and closed loop.
Diaphragm units
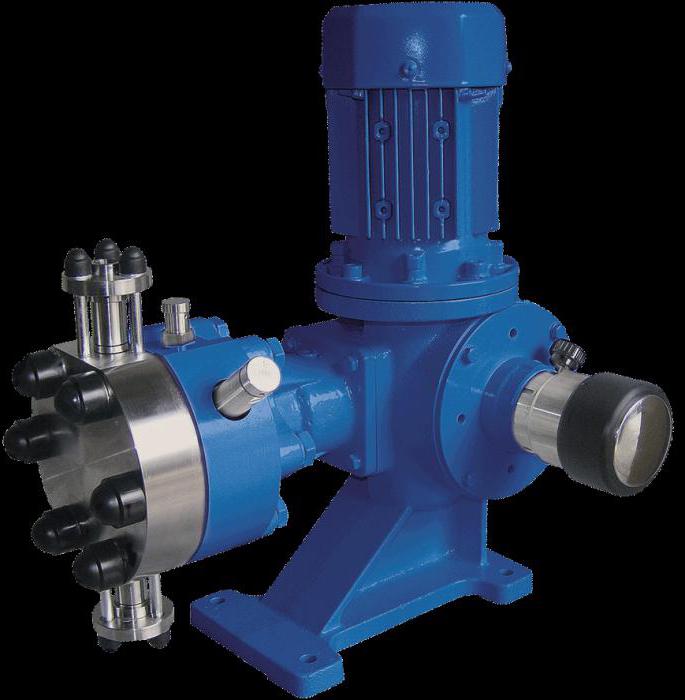

This is a volumetric pump in which a flexible plate fixed at the edges of the structure performs the function of the working body. To a certain extent, it acts as a piston. The membrane bends during operation, which leads to fluid displacement. In this case, the force impact can be different. For example, it is practiced using mechanical drives, hydraulics, and pneumatic devices that deform the plate by changing the pressure in the working cavity. Due to the absence of gearboxes and motors, metering pumps are considered the safest and most reliable. This is especially important in the maintenance of flammable liquids, since the function of the unit has no prerequisites for the formation of a spark.
Batch dosing Dosing dosing is based on pulsed delivery, after which this dose is skipped for a specified period of time. Solenoid metering pumps They have the longest history, but their use is very limited. The reason for the increasingly limited market share of the solenoid metering pumps is the inefficient control, which is reflected in the presence of pulsations in the head and flow of the dosed substance.
Pumps with an asynchronous motor They are characterized by the presence of two adjustment options. The first is shown in FIG. By changing the stroke of the piston, only the amount of the administered dose changes. The process is time independent. In the second embodiment of FIG. 9 changes the dosing time, as well as its quantity. It is used more often because it offers great regulatory options as well as greater accuracy. At the same time, it is characterized by the unevenness of the administered doses, i.e. with big ripples. Therefore, asynchronous motor pumps should not be used for viscous fluids, fluids containing gas, as well as for systems with a long suction pipe.
Plunger models
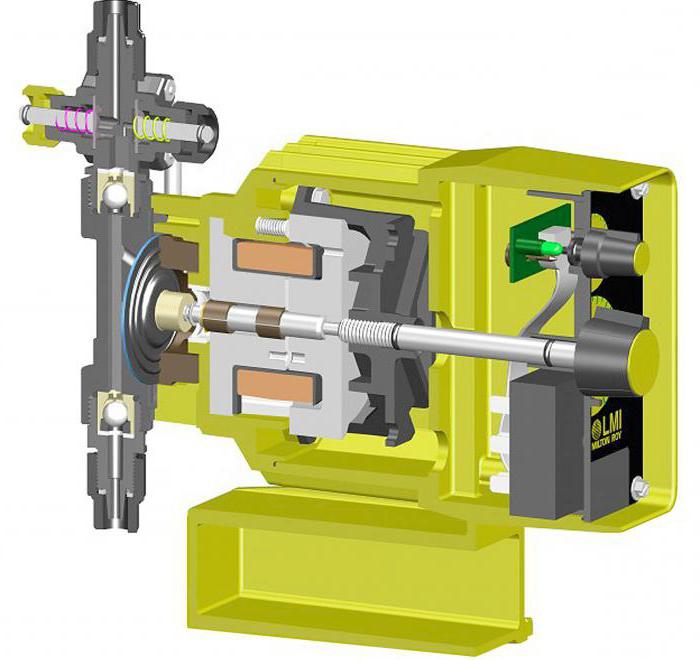
This is a type of reciprocating hydraulic machines based on reciprocating movements. The valve distribution system does not allow the use of such units for reverse action, which distinguishes them from other volumetric devices. The reverse movement of the piston in the pipeline leads to the closure of the valve, which prevents the leakage of medium into the channel. At the same time, the valve on the discharge side opens, and through it, the liquid escapes to the receiving point. In the process, dosing provides an uneven speed of fluid movement, which causes its main drawback. The spasmodic effect is compensated for in various ways, including by introducing several piston elements into the design.
Synchronous motor pumps Typically, the pump maintains maximum power, the synchronous motor runs continuously, and the suction and inertia lengths are the same - fig. When the flow changes, the suction and draft times and lengths are the same, but before each stroke the engine stops working for a certain period of time. The length of this time period is determined by the flow rate. Obviously, over time, a large non-uniform distribution of the chemical occurs.
Digital metering pumps When operating at maximum flow, the stepper motor runs continuously and the suction and discharge times are the same. When the flow of the engine decreases, it still runs continuously, the suction stroke retains its duration. On the contrary, the duration of the impact increases. This means that the digital pumps control the flow by changing the revolutions during the pressure stroke - fig. There is every reason to argue that digital metering pumps offer the best features and control capabilities.
Unit marking
If the structural design of the units are carried out in accordance with the requirements of a specific form factor, then in terms of functional content and controls mechanisms, manufacturers develop common standards. So, the ND metering pump provides for manual regulation of fluid transfer from the moment the unit stops. If the system is provided with the possibility of automatic and remote monitoring, then the equipment is assigned the designation NDE.
Since they usually work with expensive chemicals, higher accuracy ensures their efficient use, creating significant economic benefits from chemical and energy conservation. At the same time, the optimum performance of digital metering pumps ensures trouble-free operation with viscous fluids, for example. Some designs are based on the installation of a double membrane and leakage sensor. Thus, maintenance specialists receive information when the main diaphragm ruptures, and also continue to operate the pump with the second diaphragm.

Also, manufacturers indicate a dosing index, which averages 1-2.5. There are also devices in which this indicator is not observed at all. As a rule, models with an initial index do not have a heating jacket, and the highest level of metering accuracy is characterized by the presence of a shut-off or flushing fluid in the inlet design. This classification also applies to all types of aggregates. For example, a metering plunger pump ND can have both a first accuracy index and a second.
The solution is used in critical continuous processes in which stopping the metering pump is undesirable and even possible. Logically, the most important condition is that they do not react with the transferred chemicals. In the transfer part of the pump are used: polyethylene, polypropylene, teflon or stainless steel. Another important feature when choosing a metering pump is the correct choice of system accessories.
This is a very wide range of elements, including: suction valves with level sensors for the suction tank, suction tanks, deaerators, leak sensors, auxiliary pressure valves, injectors for injection, etc. Modern communication capabilities The release of one dosing pump consists of three stages: First step: calculate the pump flow rate and then fill it. Produce the pump at a rate of 100% flow rate. Thus, it is deaerated and its suction lines are filled. Step Two: Calibrate the pump.
